SERVLETS AND JDBC
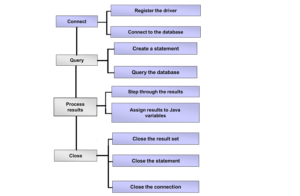
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity, which is a standard Java API for database connectivity between the Java programming language and a wide range of databases. The JDBC library includes APIs for
- Making a connection to a database.
- Creating query statements.
- Executing queries in the database.
- Viewing & Modifying the resulting records.
The JDBC API provides the following interfaces and classes −
- DriverManager: This class matches connection requests from the java application with the database driver and establishes a database Connection.
- Driver: This interface handles the communications with the database server.
- Connection: This interface has all methods to connect to the database and execute SQL queries
- Statement: interface to create SQL statements. Statement types:
- Static SQL statements (Statement interface),
- precompiled SQL statements (PreparedStatement interface), and
- stored SQL procedures (CallableStatement interface)
- ResultSet: These objects hold data retrieved from a database after executing an SQL query using Statement objects.
- SQLException: This class handles any errors that occur in a database application.
Working of JDBC
HTML, SERVLETS AND JDBC
Steps involved in creating an application to submit information to a servlet through form, accessing a database from the servlet and returning the result to client browser as a HTML page.
Steps:
Client Browser
- Create the HTML form to receive the required data
- On submit, send data to appropriate servlet in server
Server Servlet
- Receive the data from HTML form
- Construct the SQL Query
- Establish connection to the database and execute the query
- Retrieve result from the database.
- Close database connection.
- Create the HTML response page and send to client browser
Client Browser
- Display the HTML page received from the server.
Create HTML Form to submit data

<!– Simple program to demonstrate JDBC access –>
<!– Form to submit Department name to server –>
<!– html forms –>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Forms and Servlets</title>
<style>
label
{
font-family:vivaldi;
font-size:x-large;
letter-spacing:2px;
line-height:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
// Servlet Name – JDBC_DC
<form method=”GET” action=”JDBC_DC”>
<center>
<h2>HTML, Servlets and Database</h2></br>
<label>Enter Department Name </label>
<input type=”text” Name=”DN” tabindex=1/>
<br/><br/>
<button class=”btn” type=”button ” >Get Code!!! </button>
</center>
</form>
</body>
</html>
// Servlet Program
// Servlet to receive form data, access database and generate response to client
// JDBC – Database name: XEPDB1
// Table: DC (name varchar(20), code varchar(20))
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBC_DC extends HttpServlet
{
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
{
//setting the content type
res.setContentType(“text/html”);
//create the stream to write the data
PrintWriter pw=res.getWriter();
// Receive data from HTML Form
String D = req.getParameter(“DN”).trim();
//writing html in the stream
pw.println(“<html><body><h2>”);
pw.println(“<center>”);
pw.println(“Dept = “+D+”<br/>”);
try
{
// Establish connection with database
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(“jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/XEPDB1”, “<username>”, “<password>”);
String qry = “SELECT * FROM DC WHERE name ='”+ D +”‘”;
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(qry);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
pw.println(“Code = “+rs.getString(2)+”<br/>”);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
pw.println(“</center>”);
pw.println(“</h2></body></html>”);
//closing the stream
pw.close();
}
}
OUTPUT

